Sustainability
Sustainability as envinronmental initiative
Solutions that transcend and create solutions forming opportunities.
“Take CO2ntrol”



Sustainability: design and application
Aims to create products, services, and environments that minimize negative environmental and social impacts, emphasizing resource efficiency, waste reduction, and long-term well-being.
Examples of Sustainable Design Applications:
– Buildings;
Green buildings, energy efficient lighting, renewable energy systems, water-efficient fixtures, etc.
– Products;
Durable, recyclable, and reusable products, eco-friendly packaging, and products made from sustainable materials.
– Transportation;
Electric vehicles, public transportation, and transportation sharing programs.
– Agriculture;
Sustainable farming practises, organic agriculture, and reducing food waste.
“There is no higher luxury than being one with nature”.
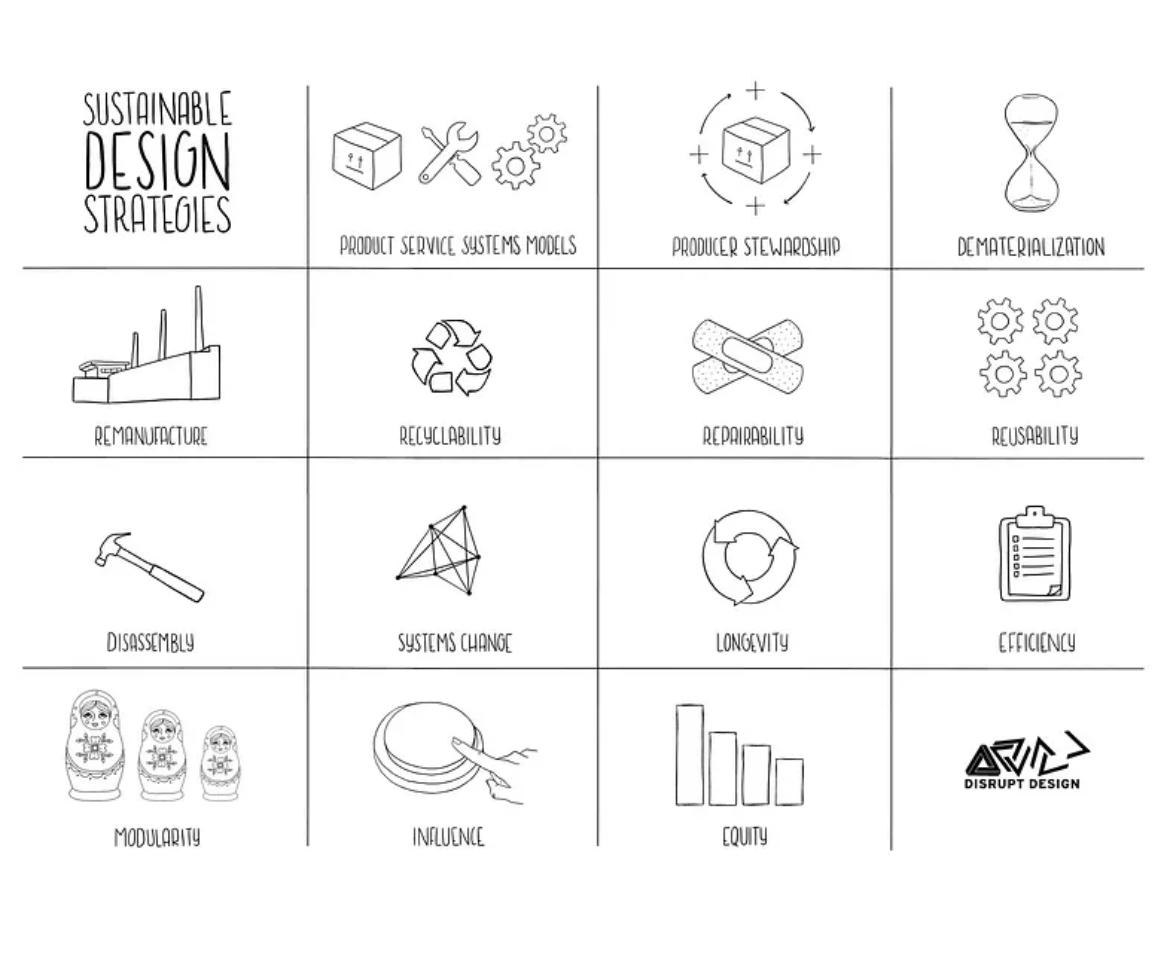
Sustainable Design Strategies
To create products and services that have considered the environmental, social, and economic impacts from the initial phase through the end of life.
EcoDesign (Green design) is a core tool in the matriax of approaches that enables the ‘Circular Economy’.

Global warming is affecting the economies, travels & industries globally.
The wider effect and impact of carbon emissions effects the Earth’s climate systems.
Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes of Earth’s climate.


Sustainability Strategies. Addressing the ‘Climate Change’
To develop sustainability strategies as an intentional guide to help manage the effect on environmental, economic, and social systems.
These strategies are a crucial element to an organization’s success and can help enhance profitability, expansion, and employee experience.
Environmental Sustainability;
Efforts to reduce environmental impact, such as minimising waste, conserving natural resources, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting biodiversity.
Economic Sustainability;
Ensuring that the economic actions are viable and beneficial in the long term, focusing on responsible resource management, efficient operations, and innovation that contributes to a sustainable economy.
Social Sustainability;
Promoting fair labour practices, community engagement, inclusivity, and ensuring that the needs of current and future generations are met without compromising cultural and societal values.
Corporate Governance and Ethics;
Establishing transparent, ethical, and accountable practices in decision-making and operations.
Measurement and Reporting;
Developing metrics to measure sustainability performance and regularly reporting progress towards sustainability goals.
“A well-defined sustainability strategy helps organisations contribute positively to the planet and society and achieve long-term business success by reducing risks, driving innovation, enhancing brand reputation, and building trust among stakeholders”.
Environmental Benefits
Reduced Carbon Footprint: Lower greenhouse gas emissions through energy-efficient practices and renewable energy sources.
Conservation of Resources
Efficient use of water, energy, and other natural resources, minimising waste and promoting recycling and reuse.
Biodiversity Protection
Practices that protect ecosystems and biodiversity include sustainable sourcing and habitat conservation.
Cost Savings
Reduction in energy, water, and material costs through efficiency improvements.
Improved Competitivness
Enhanced brand value and competitive advantage in markets where consumers value sustainability.
Innovation
Development of new sustainable products and services, opening up new markets and customer segments.
Risk Management
Mitigating risks associated with resource scarcity, climate change, and fluctuating energy costs.
Public Image
Enhanced reputation and brand loyalty among consumers and the broader community.

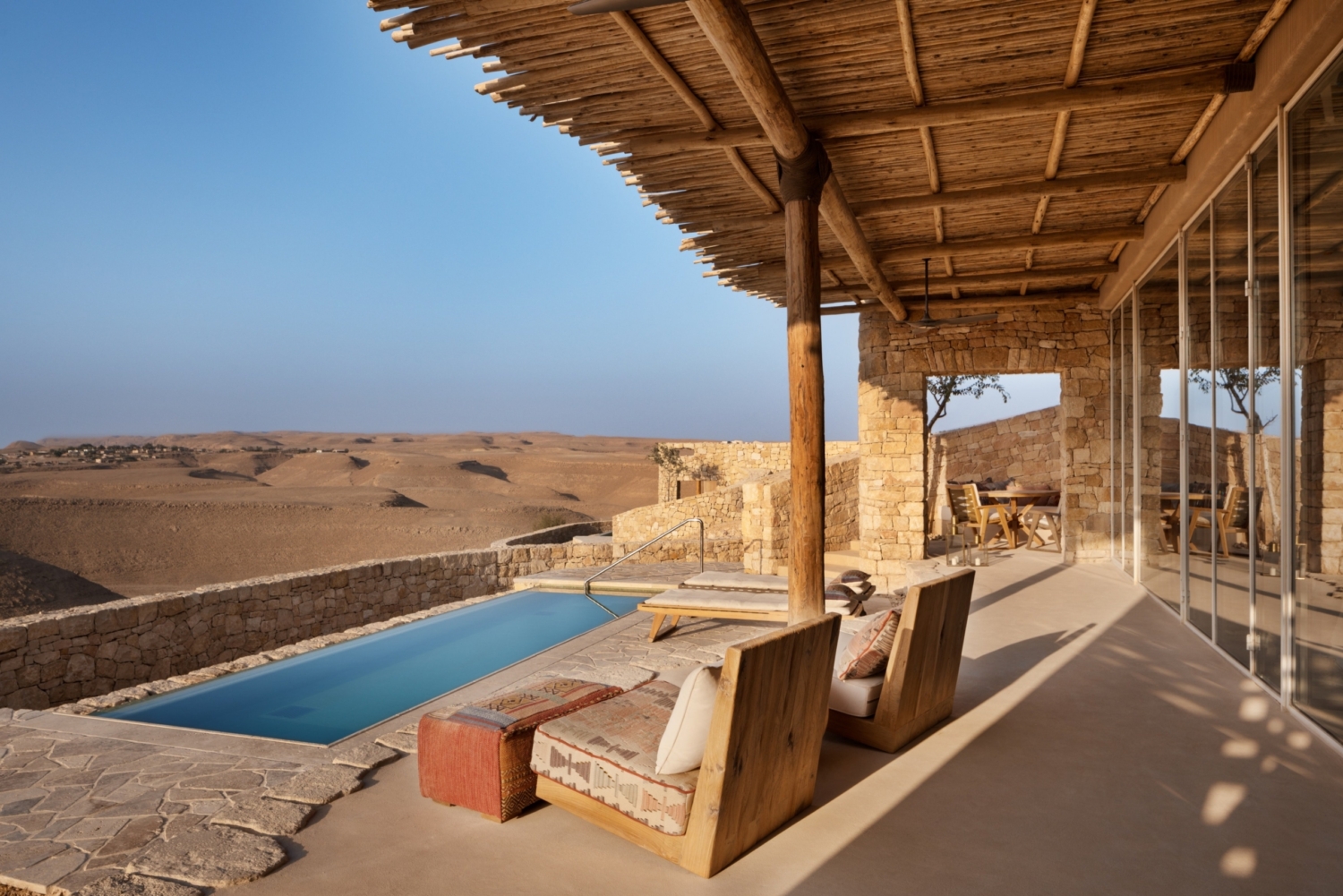
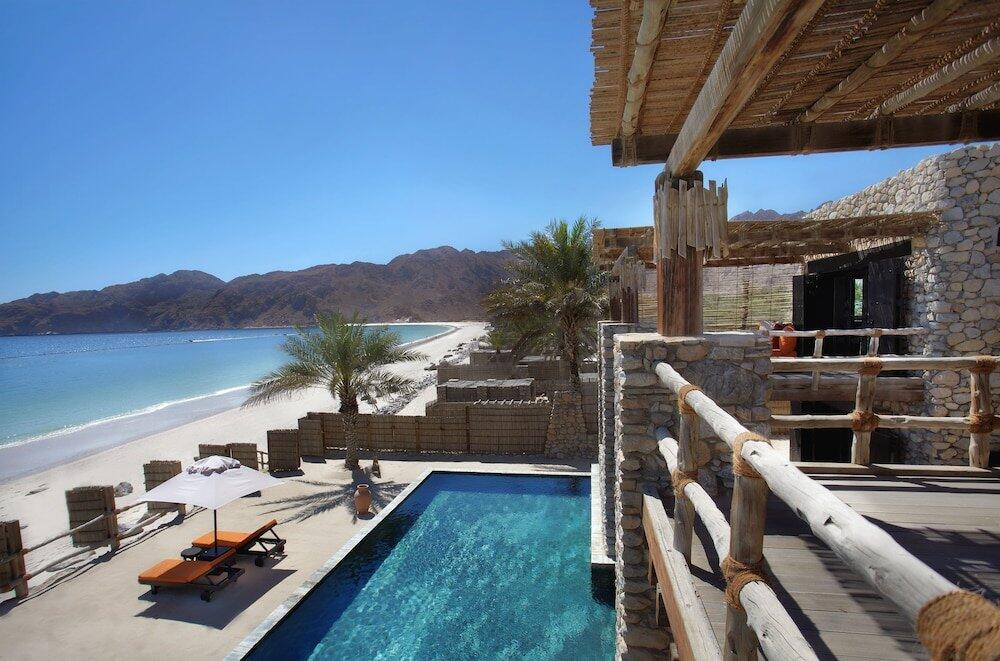
“Travel to awaken experience, emotions and exposure to new cultures and locations”.
The goal is not only to minimize our impact, but to actually have a positive effect on the environments we settle in. That means actively contributing to the conservation of wildlife and the regeneration of the natural habitats around our lodges. It means embracing local culture and heritage, celebrating traditional food and art, and supporting the development of the local community.
To explore our planet, and all the beautiful, natural sights it has to offer. Responsible travellers recognize that the luxury of that experience comes hand in hand with the responsibility to preserve it. Because if we don’t, there won’t be much left to explore or discover. This is what sustainable tourism is all about.
Mobilizing for a sustainable future
Actions to drive Resilience.
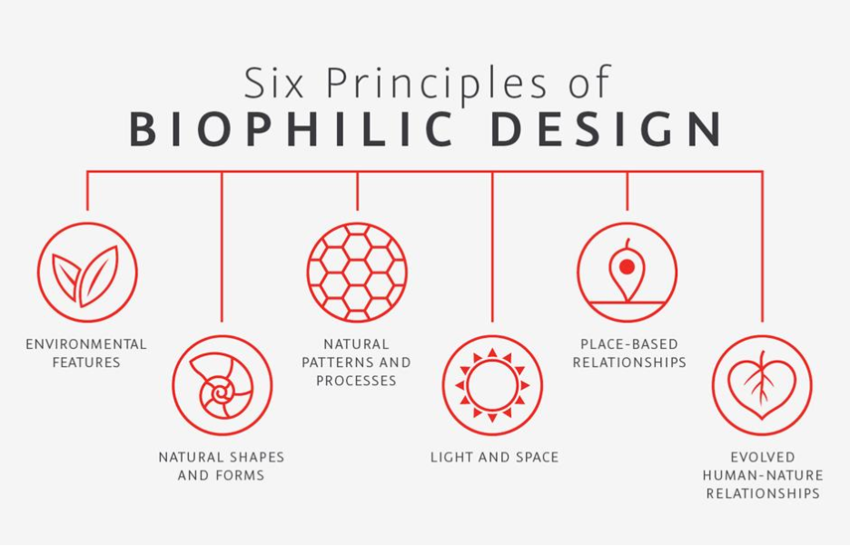
‘Biophilic Design as design & project strategy to address ‘WELL-being Solutions’.
